Introductory Paragraph:
Have you ever wondered what truly sets successful individuals apart? It’s not just IQ, academic degrees, or technical expertise—it’s emotional intelligence (EI). Coined by Daniel Goleman, Emotional Intelligence Framework emphasizes mastering self-awareness, empathy, and interpersonal skills to thrive in today’s world. Whether you’re leading a team, managing relationships, or simply striving for personal growth, this framework is your blueprint to success. Let’s dive into Goleman’s transformational model and explore how it can revolutionize the way you connect, lead, and live.
The Ultimate Guide to Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework
When we talk about success in life and work, Emotional Intelligence (EI) often takes center stage. Daniel Goleman, a psychologist and journalist, popularized the concept through his groundbreaking book Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. In this article, we’ll unpack his framework, understand its five key components, and learn practical ways to apply it in everyday life.
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Emotional Intelligence Meaning : At its core, emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage our emotions while effectively navigating the emotions of others. Think of it as your personal GPS for emotional and social landscapes. While technical skills are important, EI enables you to harness the human connection that fuels both personal and professional relationships.
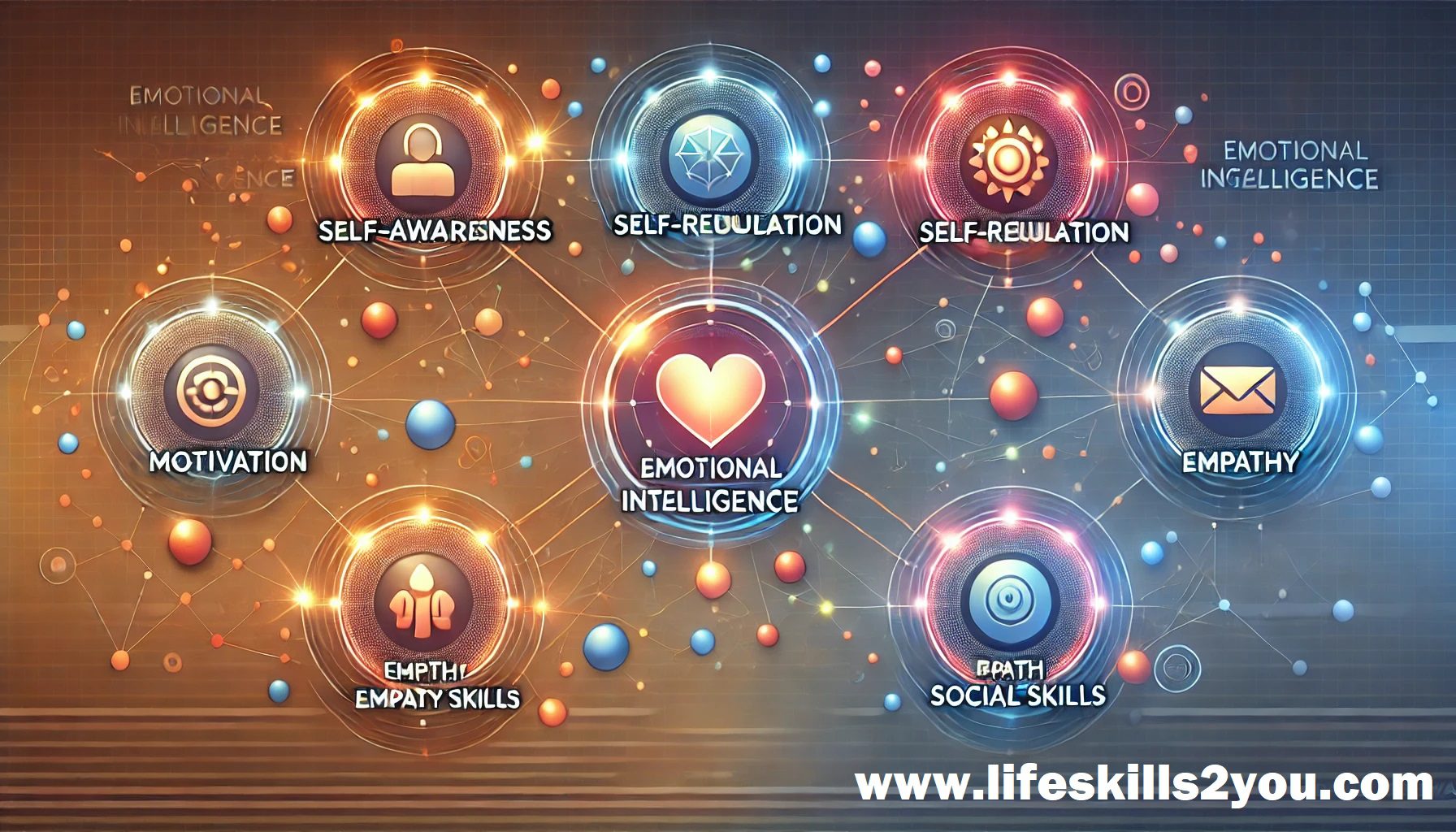
The Five Pillars of Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework
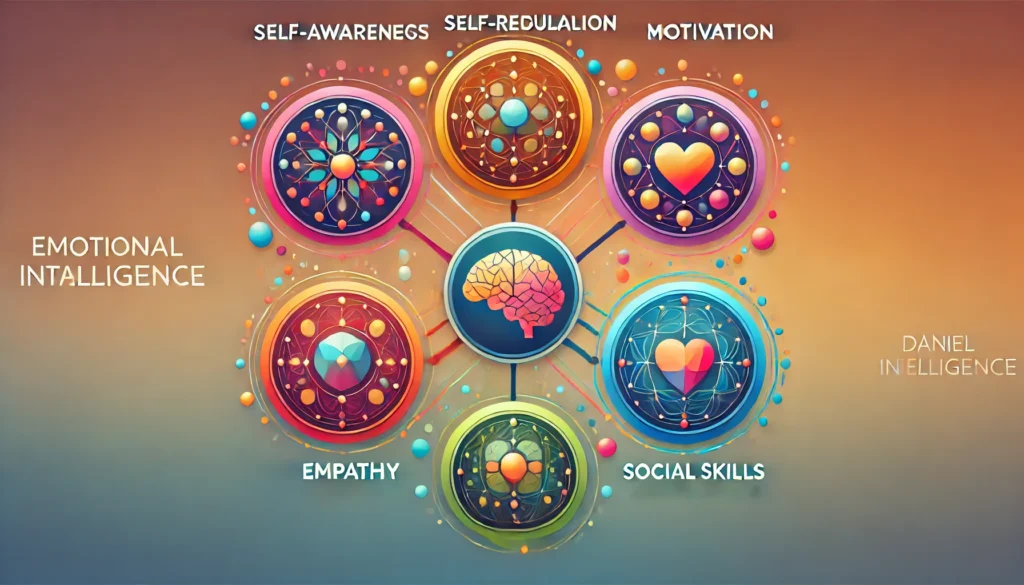
1. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of emotional intelligence. It’s all about understanding your emotions and how they affect your thoughts and actions. Imagine you’re a captain steering a ship—without awareness of the weather (your emotions), you risk losing direction.
“Knowing yourself is the beginning of all wisdom.”
Aristotle
2. Self-Regulation
Emotions can be like wild horses—if left unchecked, they can lead to impulsive decisions. Self-regulation helps you rein in those impulses and maintain control even in stressful situations.
3. Motivation
Motivation within the EI framework refers to intrinsic drive—the internal desire to achieve goals for personal satisfaction, not external rewards. It’s the fuel that powers perseverance.
4. Empathy
Empathy is your ability to step into someone else’s shoes and truly understand their feelings. It’s the heart of emotional intelligence, building bridges of connection and trust.
5. Social Skills
Strong social skills allow you to build rapport, resolve conflicts, and lead effectively. Whether networking or managing teams, these skills can turn interactions into lasting relationships.
Why Emotional Intelligence Matters More Than Ever
In today’s fast-paced world, technology connects us more than ever before, but it also leaves room for miscommunication. EI fills this gap, ensuring clarity, compassion, and collaboration. Whether you’re leading a team, building a family, or chasing dreams, emotional intelligence is your secret weapon for resilience and growth.
Applications of Goleman’s Framework in Everyday Life
- Workplace Success:
Employees with high EI excel in teamwork, leadership, and adaptability. They turn conflicts into opportunities and inspire others to perform better. - Personal Relationships:
Emotional intelligence deepens connections, builds trust, and enhances communication. It’s the glue that holds meaningful relationships together. - Mental Well-Being:
Practicing EI reduces stress, promotes mindfulness, and fosters a positive mindset.
Resources to Explore Further
To gain a deeper understanding of Goleman’s framework, check out:
How to Develop Emotional Intelligence Using Goleman’s Framework
Understanding the principles of emotional intelligence is just the beginning; developing these skills requires consistent effort and intentional practice. Let’s explore actionable strategies for enhancing each pillar of Goleman’s EI framework.
1. Building Self-Awareness
To truly grow in self-awareness, you must learn to tune into your emotional state, much like fine-tuning a radio station. Here are some techniques to strengthen your emotional insight:
- Keep a Daily Journal: Spend 5-10 minutes jotting down your emotions, what triggered them, and how you reacted. Over time, patterns will emerge, helping you recognize recurring emotional themes.
- Meditate: Mindfulness meditation is a powerful tool for observing your thoughts and emotions without judgment.
- Ask for Honest Feedback: People close to you can often see aspects of your emotional reactions that you may overlook. Seek their input and reflect on it constructively.
“Everything that irritates us about others can lead us to an understanding of ourselves.”
Carl Gustav Jung
2. Mastering Self-Regulation
Self-regulation is like learning to ride the waves of emotion without letting them crash over you. It doesn’t mean suppressing emotions; it means managing them effectively.
- Pause Before Reacting: In tense situations, count to ten before speaking. This simple act can prevent impulsive outbursts.
- Adopt a Growth Mindset: View challenges and setbacks as opportunities to learn rather than threats.
- Practice Gratitude: When emotions feel overwhelming, focus on things you’re grateful for. Gratitude shifts your perspective and helps calm the storm.
3. Cultivating Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation keeps you going even when external rewards are absent. Think of it as the spark that ignites your passion and fuels your perseverance.
- Define Your ‘Why’: Take time to clarify your purpose. Why do you wake up each day? Aligning your actions with your core values creates lasting motivation.
- Visualize Success: Picture yourself achieving your goals. This technique can make your aspirations feel more tangible and within reach.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize and reward yourself for progress, no matter how minor. Small victories keep the momentum alive.
4. Strengthening Empathy
Empathy is the bridge that connects your world to someone else’s. When practiced, it can transform relationships and foster genuine human connections.
- Listen to Understand, Not to Reply: Most of us listen with the intent to respond. Instead, focus on truly understanding the other person’s perspective.
- Mirror Emotions: Acknowledge what the other person is feeling by reflecting their emotions. For example, say, “It sounds like you’re feeling frustrated.”
- Volunteer or Engage in Diverse Communities: Stepping outside your comfort zone and engaging with people from different walks of life broadens your understanding of their experiences.
“Kindness is a language which the deaf can hear and the blind can see.”
Mark Twain
5. Refining Social Skills
Social skills encompass the art of communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution. Strong social skills turn conversations into connections and colleagues into allies.
- Practice Empathetic Communication: Use phrases like “I understand how you feel” to show you value the other person’s perspective.
- Learn Nonverbal Communication: Body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions often speak louder than words. Pay attention to these cues during interactions.
- Master the Art of Feedback: Provide constructive feedback that encourages growth. Instead of saying, “You did this wrong,” try, “Here’s how we can improve next time.”
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Leaders with high emotional intelligence stand out because they inspire trust, adapt to challenges, and nurture their teams. In Goleman’s framework, EI is not just a “nice-to-have” for leaders—it’s essential.
- Inspire Through Empathy: A leader who understands their team’s emotions can better motivate and support them.
- Promote Collaboration: Strong social skills allow leaders to mediate conflicts and foster a culture of cooperation.
- Adapt and Thrive: Self-awareness and regulation equip leaders to handle crises with grace, making them role models for resilience.
Real-World Applications of Emotional Intelligence
In the Workplace:
Imagine a workplace conflict where two employees disagree over a project deadline. A manager with strong EI would empathize with both perspectives, mediate a solution, and ensure that both employees feel heard and valued.
In Personal Relationships:
Consider a situation where a friend is upset but hesitant to talk about it. By tuning into their nonverbal cues and expressing empathy, you create a safe space for them to open up.
In Parenting:
Parents who practice emotional intelligence raise emotionally resilient children. Teaching kids to identify and manage their emotions sets them up for lifelong success.
Challenges in Developing Emotional Intelligence
While the benefits of EI are undeniable, the journey to mastering it isn’t always smooth. Common challenges include:
- Overcoming deeply ingrained habits, like reacting impulsively.
- Balancing empathy with assertiveness to avoid emotional burnout.
- Consistently practicing self-awareness in a busy world.
Remember
Growth in EI is a marathon, not a sprint. The key is persistence.
Conclusion
Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework is more than just a theory; it’s a roadmap for personal and professional success. By mastering self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, you can elevate every aspect of your life. Emotional intelligence is not a talent reserved for the few—it’s a skill anyone can learn. As Goleman wisely said, “The rules for work are changing. We’re being judged by a new yardstick: not just how smart we are, but also how well we handle ourselves and others.”
Call to Action:
Thank you for exploring this comprehensive guide to Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework. If you’re eager to learn more, check out our other engaging articles. Dive into our blog to uncover more tips and strategies for personal and professional growth. Ready to transform your life? Click Our Blog and How-to Guide to begin your journey. Happy reading!
FAQs on Daniel Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework
1. What is emotional intelligence (EI)?
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and influence emotions in oneself and others.
2. What are the five pillars of Daniel Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework?
The five pillars are:
1. Self-Awareness: Recognizing and understanding your own emotions.
2. Self-Regulation: Managing your emotions and impulses effectively.
3. Motivation: Using emotional factors to achieve goals and stay focused.
4. Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others.
5. Social Skills: Building and maintaining healthy interpersonal relationships.
3. Why is emotional intelligence important?
Emotional intelligence helps individuals improve communication, build better relationships, manage stress, and make thoughtful decisions, making it crucial for personal and professional success.
4. How does self-awareness improve emotional intelligence?
Self-awareness allows individuals to understand their emotional triggers, strengths, and weaknesses, enabling better decision-making and emotional control.
5. Can emotional intelligence be learned or improved?
Yes, emotional intelligence is not fixed and can be developed through self-reflection, practice, and emotional skill-building exercises.
6. How is emotional intelligence different from IQ?
While IQ measures cognitive abilities like problem-solving and reasoning, EI focuses on understanding and managing emotions, making it a complementary skill set.
7. What role does empathy play in emotional intelligence?
Empathy allows individuals to connect with others on an emotional level, fostering trust and improving communication in personal and professional relationships.
8. Why is self-regulation important in the workplace?
Self-regulation helps individuals manage stress, control impulsive behaviors, and maintain professionalism, enhancing teamwork and productivity.
9. How does emotional intelligence impact leadership?
Leaders with high EI are better at inspiring teams, resolving conflicts, and adapting to change, making them more effective and respected.
10. What are practical ways to enhance social skills within the emotional intelligence framework?
Improving social skills involves active listening, effective communication, conflict resolution, and showing genuine interest in others’ perspectives.